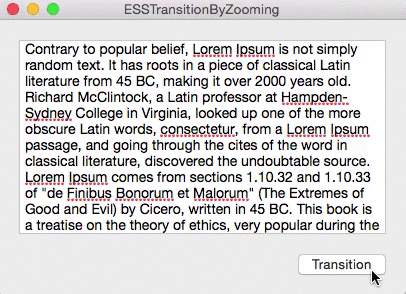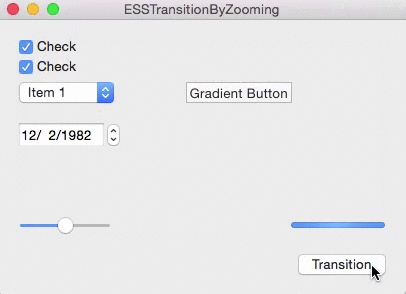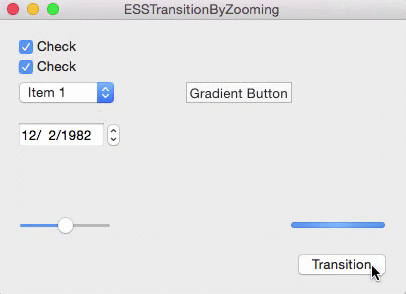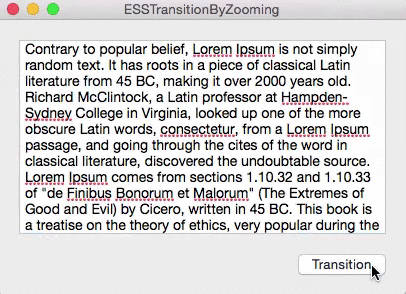
For Briefly, I needed a nice, subtle animation for switching between the detail soundtrack view and the reorderable list view. In OS X Yosemite 10.10.3’s Photos.app, I noticed something I liked very much.
When going into an album, for example, the current view is zoomed out of focus and the new view is zoomed in.
NSView+ESSViewCategory
I wrote a little category on NSView to do just that, it’s a one liner (ironically, in this pic, it’s more than one line) :

It’s pretty self-explanatory. You pass in the view you want to transition from and the one you want to transition to, the type of transition (zooming in or out), the duration and an optional completionHandler that’s called when the animation ends.
Alternatively, it’s also available as an instance method where the view you call this on will be passed into the class method as fromView:

The Views
For the transition to work, fromView has to be in a view hierarchy, toView shouldn’t. They should be the same size, otherwise more work on your part is necessary (which I had to do in Briefly because the NSPopover the views reside in resizes before / after the transition), but either way the code provided should give you a nice head start.
fromView’s superview is temporarily set to have a CALayer to make use of Core Animation during the transition. After the animation ends, the superview’s wantsLayer – state is reset to what it was before the animation. If we didn’t do this, the animation would appear sluggish.
ESSViewZoomTransition
As you can see in the gif above, there are two types of the transition:
– ESSViewZoomTransitionZoomOut – the transition from the textView to the view with the checkboxes.
– ESSViewZoomTransitionZoomIn – the transition from the checkbox-view to the textView
How To Use NSView+ESSViewCategory
You’ll have to first add the NSView+ESSViewCategory.h and *.m files to your project.
Please note that the category imports <Quartz/Quartz.h> for Core Animation’s CAMediaTiming class, so you might have to add that framework to your project, too.
fromView
It has to be inside of a view hierarchy. Fades out during the transition.
toView
Can be in a different xib file (for example, a NSViewController) or in the same as fromView. It’s important that it is not already on screen somewhere. Fades in during the transition.
Once you have set up your views, either call the class method and pass fromView and toView as well as the other parameters or call the instance method on fromView.
How It Works
The method creates an NSImage of both toView and fromView, puts them into two NSImageViews that have the same frame as the views and animates those two NSImageViews accordingly (calling imageView.animator.frame = …; and imageView.animator.alphaValue = …; )
Because fromView’s superview temporarily gets a CALayer, .animator is powered by Core Animation, which makes for a much smoother animation than doing the same without a layer-backed view.
 Creating an NSImage of toView.
Creating an NSImage of toView.
So the views themselves aren’t actually resized, they’re just screenshotted, removed from view as we place the NSImageView on top of it, creating the illusion that nothing happened. Then we animate the NSImageViews and insert toView after the animation is done, removing both NSImageViews.
The Source Code
The repository (a sample OS X app) is available on Github.
It was developed (and tested) on OS X Yosemite 10.10.3 using Xcode 6.3.1, but should work on earlier versions of the operating system.
I have some more source code available here (or directly on my github profile page) if you’re interested. If you have any questions or feedback regarding my open source projects, please be sure to mail or tweet me – I’m looking forward to your feedback!
Enjoy!








